- Dew Point Meters
- Gas Analysers
- Portable Gas Detector
- Moisture And Dew Point Analyzer
- Dust/Opacity Monitor
- Gas Monitoring Systems
- Gas Leak Detectors
- Gas Transmitters
- VOC Leak Detector
- Air Quality Monitoring System
- Online Continuous Emission Monitoring System-OCEMS
- Dew Point Monitors
- Gas Detector
- Opacity Monitor
- Portable Flue Gas Analyzer
- Online SOX & NOX Gas Analyzer
- Methane Gas Leak Detector
- Hydrogen Purity Analyzer
- Gas Purity Analyzer
- Effluent Monitoring Systems
- Producer Gas Analyzer
- Gas Detector Calibration Service
- Portable Gas Monitors
- Gas Sensor Transmitter
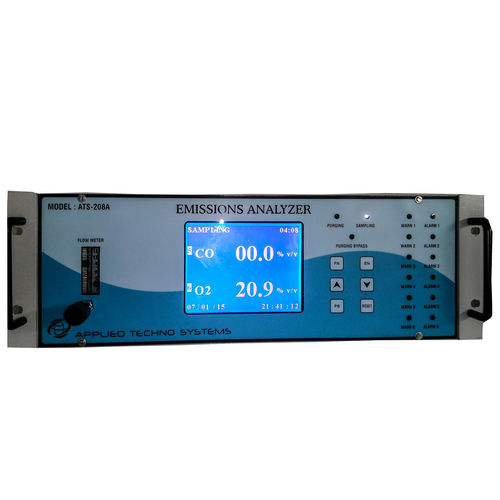
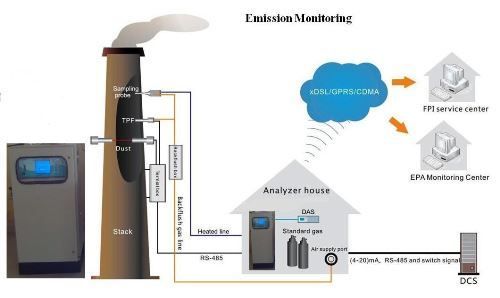
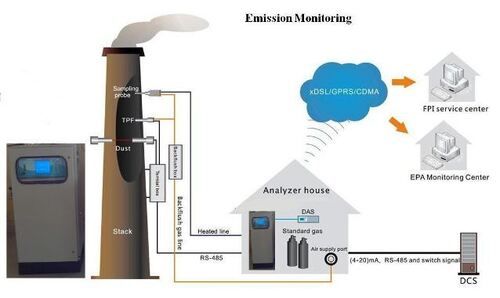
Environmental Emissions Monitoring Systems
Price 1050000 INR/ Unit
Environmental Emissions Monitoring Systems Specification
- Resolution
- 0.1 ppm
- Power Supply
- 220 V AC, 50 Hz
- Application
- Industrial Emissions Testing, Air Quality Monitoring
- Response Time
- 10 seconds
- Number of Specimens
- 1-3 Channels
- Interface Type
- RS232 / USB / Ethernet
- Product Type
- Monitor
- Color
- Grey
- Equipment Type
- Environmental Emissions Monitoring Systems
- Automation Grade
- Automatic
- Specimen Size
- Standard
- Display Type
- Graphics Display
- Test Range
- 0.1 ~ 1000 ppm
- Operating Voltage
- 220 V AC
- Measuring Range
- 0.1 ~ 1000 ppm
- Max Height
- 400 mm
- Gas Pressure
- 0.1~0.6 MPa
- Mounting Type
- Wall / Rack Mounted
- Humidity
- 5% ~ 95% RH (Non-condensing)
- Frequency
- 50 Hz
- Temperature
- -10C ~ 50C
- Port Size
- 1/4 inch
- Features
- Continuous Monitoring, Real-Time Data, Multi-parameter Detection
- Usage
- Industrial
- Capacity
- Up to 3 probe connections
- Machine Weight
- 90 kg
- Test Speed
- 5-50 mm/min
- Test Width
- 150 mm
- Test Stroke
- 300 mm
- Control Mode
- Automatic
- Communication Protocols
- Modbus, TCP/IP
- Color
- Grey
- Product Type
- Monitor
- Data Storage
- Internal Memory with Export
- Data Logging Interval
- Configurable
- Sensor Type
- Electrochemical and Infrared Sensors
- Compliance Standard
- Meets National and International Emission Standards
- Alarm
- Visual and Audible Alarm
- Enclosure Rating
- IP54
- Power Consumption
- <60W
Environmental Emissions Monitoring Systems Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Unit
- Payment Terms
- Cash Advance (CA), Cash in Advance (CID), Cheque
- Packaging Details
- As Per Customer Requirement
- Main Export Market(s)
- Asia, Australia, Central America, North America, South America, Eastern Europe, Western Europe, Middle East, Africa
- Main Domestic Market
- All India, South India, Central India, West India, North India, East India, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Manipur, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chandigarh, Daman and Diu, Goa, Jharkhand, Odisha, Punjab, Assam, Delhi, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Arunachal Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Nagaland, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Tripura, Pondicherry, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, West Bengal
- Certifications
- An ISO 9001:2015 Company
About Environmental Emissions Monitoring Systems
Environmental Emissions Monitoring Systems (CEMS) are technologies and tools used to measure, analyze, and track pollutants released into the air, water, or soil by industrial processes, transportation, and other sources. These systems are essential for ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, assessing the impact of emissions on air quality, and enabling industries to monitor their environmental footprint.
- Continuous Emission Monitoring: EEMS often include Continuous Emissions Monitoring Systems (CEMS) that provide real-time data on pollutants such as carbon dioxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NO), sulfur dioxide (SO), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from sources like smokestacks, industrial plants, and power stations.
- Data Collection and Reporting: These systems are designed to collect data continuously or at frequent intervals, which is then analyzed and reported. This data helps regulators ensure that industries comply with emission limits and environmental standards.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Many EEMS provide real-time feedback, alerting operators or environmental authorities when emissions exceed permitted levels. This helps mitigate environmental damage by enabling timely corrective actions.
- Data Logging and Storage: EEMS typically store data for long periods, allowing for historical analysis, trend monitoring, and regulatory reporting. This is particularly important for compliance with laws that require records to be kept for a specific duration.
- Integration with Regulatory Standards: EEMS are designed to measure pollutants according to established standards, such as those set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the U.S., the European Union Emission Standards, or other local environmental authorities
Advanced Industrial Emissions Monitoring
Designed for high-performance, continuous monitoring, this system is ideal for various industrial emissions testing and air quality monitoring applications. Its multi-parameter detection ensures comprehensive analysis, while robust electrochemical and infrared sensors provide accuracy and rapid response. The automatic control mode and graphical interface streamline operations, making the monitor suitable for both wall and rack mounting in demanding environments.
Seamless Data Handling and Connectivity
With internal memory for data storage and export functions, users can confidently retrieve and manage monitoring results. Configurable data logging intervals and compatibility with RS232, USB, Ethernet, Modbus, and TCP/IP guarantee seamless integration into existing facility management systems for real-time reporting, analysis, and regulatory compliance.
Built for Industrial Reliability and Safety
The IP54-rated enclosure ensures dependable performance in harsh industrial settings. Visual and audible alarms provide immediate notification of emission threshold exceedances, enhancing workplace safety. With a capacity for up to three probe channels and adaptable to a variety of specimen sizes, this system offers versatile monitoring to support diverse operational requirements.
FAQ's of Environmental Emissions Monitoring Systems:
Q: How does the environmental emissions monitoring system detect and measure pollutants?
A: The system uses a combination of electrochemical and infrared sensors to detect and quantify various gas concentrations within a 0.1 to 1000 ppm range. It provides accurate measurements with a resolution of 0.1 ppm and a response time of ten seconds or less.Q: What is the process for exporting and managing collected data?
A: Collected data is stored in the unit's internal memory and can be exported through multiple interfaces such as RS232, USB, or Ethernet. Data logging intervals are configurable, enabling customized monitoring and straightforward integration with industrial management platforms via Modbus or TCP/IP protocols.Q: When should visual and audible alarms be expected to activate?
A: Alarms activate whenever emission levels exceed user-set thresholds. Both visual indicators and audible alerts immediately notify operators, allowing for swift intervention to maintain regulatory compliance and workplace safety.Q: Where can this emissions monitoring system be installed?
A: The unit is designed for industrial environments and supports flexible wall or rack-mounted installation. Its IP54-rated enclosure and robust construction ensure reliable operation in challenging conditions typical to manufacturing plants and process industries.Q: How does the system ensure reliable performance in different environmental conditions?
A: With an operating temperature range of -10C to 50C, humidity capability from 5% to 95% RH (non-condensing), and an IP54 enclosure rating, the system is engineered for longevity and reliability even in harsh industrial settings.Q: What are the main benefits of using this monitor for industrial emissions testing?
A: The system combines precision, real-time monitoring, and automated controls for maximum efficiency. Users benefit from accurate, rapid detection, enhanced safety through alarms, compliant reporting, seamless integration, and versatile data export-making it a comprehensive solution for air quality and emissions management.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Online Continuous Emission Monitoring System-OCEMS Category
Online SO2 Gas Analyzer
Price 325500.00 INR / Pack
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Pack
Usage : Emission Monitoring in Industries
Humidity : < 85%RH
Temperature : 5 to +55 Celsius (oC)
Power Supply : 230 V AC
Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS)
Price 950000 INR / Pack
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Pack
Usage : Industrial
Humidity : < 85%RH
Temperature : 15 Celsius (oC)
Power Supply : Electric
Online Continuous Emissions Monitoring Systems (OCEMS)
Price 725500.00 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Piece
Usage : Continuous Emission Monitoring
Humidity : < 85%RH
Temperature : 5 to +55 Celsius (oC)
Power Supply : 230 V AC 50Hz
Stack Emission monitor continuous Emission Analyzer
Price 400000 INR / Number
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Number
Usage : Industrial
Humidity : 85%RH
Temperature : 40 to 55 Celsius (oC)
Power Supply : Electric

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry